Pernicious anemia is a chronic form of vitamin B12 deficiency anemia caused by the body’s inability to absorb vitamin B12 effectively. Unlike dietary deficiencies, pernicious anemia is usually linked to autoimmune destruction of intrinsic factor, a protein essential for vitamin B12 absorption in the small intestine.
If left untreated, pernicious anemia can lead to serious complications, including neurological damage, cardiovascular issues, and irreversible nerve injury. Early diagnosis and lifelong treatment are crucial to prevent long-term health consequences.
This article provides a comprehensive overview of pernicious anemia, covering its causes, symptoms, risk factors, diagnosis, treatment options, and prevention strategies.
What Is Pernicious Anemia?
Pernicious anemia is a type of megaloblastic anemia characterized by the production of abnormally large, immature red blood cells due to inadequate vitamin B12 levels.
Vitamin B12 plays a vital role in:
Red blood cell formation
DNA synthesis
Neurological function
In pernicious anemia, vitamin B12 deficiency occurs not because of low intake, but because the body cannot absorb it properly.

Causes of Pernicious Anemia
The primary cause of pernicious anemia is the lack of intrinsic factor, a glycoprotein produced by the stomach’s parietal cells.
Key Causes Include:
1. Autoimmune Gastritis
The immune system mistakenly attacks:
Gastric parietal cells
Intrinsic factor itself
This autoimmune process leads to reduced vitamin B12 absorption.
2. Intrinsic Factor Deficiency
Without intrinsic factor, vitamin B12 cannot bind properly and pass through the small intestine into the bloodstream.
3. Chronic Atrophic Gastritis
Long-standing inflammation of the stomach lining results in:
Reduced stomach acid
Decreased intrinsic factor production
4. Gastric Surgery
Procedures such as:
Partial or total gastrectomy
Bariatric surgery
can remove or damage areas responsible for intrinsic factor production.
Risk Factors for Pernicious Anemia
Certain individuals are more prone to developing pernicious anemia.
Common Risk Factors Include:
Northern European descent
Age over 50 years
Autoimmune disorders (e.g., thyroid disease, type 1 diabetes)
Long-term use of acid-suppressing medications
Strict vegetarian or vegan diets
History of gastric or intestinal surgery
Pathophysiology of Pernicious Anemia
The development of pernicious anemia follows a predictable sequence:
Autoimmune destruction of gastric parietal cells
Reduced or absent intrinsic factor production
Failure to absorb vitamin B12 in the terminal ileum
Impaired DNA synthesis in bone marrow
Production of large, dysfunctional red blood cells
Reduced oxygen-carrying capacity
Over time, vitamin B12 deficiency also affects the nervous system, leading to neurological symptoms.
Signs and Symptoms of Pernicious Anemia
Symptoms may develop gradually and worsen over months or years.
General Symptoms
Dizziness or lightheadedness
Paleness of skin and mucous membranes
Gastrointestinal Symptoms
Glossitis (inflamed, smooth tongue)
Neurological Symptoms
Numbness or tingling in hands and feet
Difficulty walking
Balance problems
Memory loss or confusion
Depression or mood changes
Cardiovascular Symptoms
Chest discomfort
Increased risk of heart disease due to chronic anemia
Complications of Untreated Pernicious Anemia
If untreated, it can cause serious complications:
Permanent nerve damage
Cognitive impairment and dementia
Increased risk of gastric cancer
Heart failure due to prolonged anemia
Early detection significantly reduces these risks.
Diagnosis of Pernicious Anemia
Accurate diagnosis requires a combination of clinical evaluation, blood tests, and specialized investigations.
Blood Tests
Complete blood count (CBC): Shows macrocytic anemia
Peripheral blood smear: Large red blood cells
Serum vitamin B12 levels
Specific Diagnostic Tests
Intrinsic factor antibody test
Parietal cell antibody test
Serum methylmalonic acid (MMA)
Homocysteine levels
Additional Tests
Bone marrow examination (rare cases)
Treatment of Pernicious Anemia
Pernicious anemia requires lifelong vitamin B12 replacement therapy.
Vitamin B12 Injections
Intramuscular injections are the standard treatment
Initial loading phase followed by maintenance doses
Often required for life
Oral Vitamin B12
High-dose oral supplementation may be effective in some patients
Suitable for those who cannot tolerate injections
Monitoring
Regular blood tests
Neurological assessment
Monitoring response to therapy
Most patients experience rapid improvement in symptoms after starting treatment.
Living With Pernicious Anemia
With proper treatment, individuals with pernicious anemia can lead a normal and healthy life.
Lifestyle Tips
Adhere strictly to treatment schedules
Attend regular follow-up appointments
Monitor neurological symptoms
Maintain a balanced diet
Although dietary changes alone cannot cure pernicious anemia, adequate nutrition supports overall health.
Can Pernicious Anemia Be Prevented?
Because pernicious anemia is often autoimmune, complete prevention is not always possible. However, early detection and treatment can prevent complications.
Preventive Measures
Regular health check-ups for high-risk individuals
Monitoring vitamin B12 levels in older adults
Early evaluation of unexplained anemia or neurological symptoms
Prognosis
The prognosis of pernicious anemia is excellent with early diagnosis and consistent treatment. Most symptoms are reversible, although long-standing neurological damage may be permanent.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Is it the same as vitamin B12 deficiency?
No. Pernicious anemia is a specific type of vitamin B12 deficiency caused by impaired absorption, not inadequate intake.
2. Is it a lifelong condition?
Yes. Most patients require lifelong vitamin B12 replacement therapy.
3. Can it be cured?
It cannot be cured, but it can be effectively managed with proper treatment.
4. Are vitamin B12 injections painful?
They cause minimal discomfort and are generally well tolerated.
5. Can it cause nerve damage?
Yes. Untreated pernicious anemia can lead to permanent neurological damage.
6. Is it hereditary?
There is a genetic predisposition, but it is not directly inherited.
7. Can diet alone treat pernicious anemia?
No. Dietary vitamin B12 cannot be absorbed properly due to intrinsic factor deficiency.
8. How often are vitamin B12 injections needed?
Initially frequent, then usually once every 1–3 months for maintenance.
9. Is it very common?
It is relatively uncommon but more prevalent in older adults.
10. Can it increase cancer risk?
Yes. There is an increased risk of gastric cancer in long-standing cases.
Pernicious anemia is a serious but highly manageable condition when diagnosed early. Understanding its causes, recognizing symptoms, and adhering to lifelong treatment are essential to prevent complications. Regular monitoring and medical supervision ensure excellent long-term outcomes.
If you experience persistent fatigue, neurological symptoms, or unexplained anemia, consult a healthcare professional for timely evaluation.
#BhaloTheko
Disclaimer:
No content on this site, regardless of date, should ever be used as a substitute for direct medical advice from your doctor or other qualified clinician.
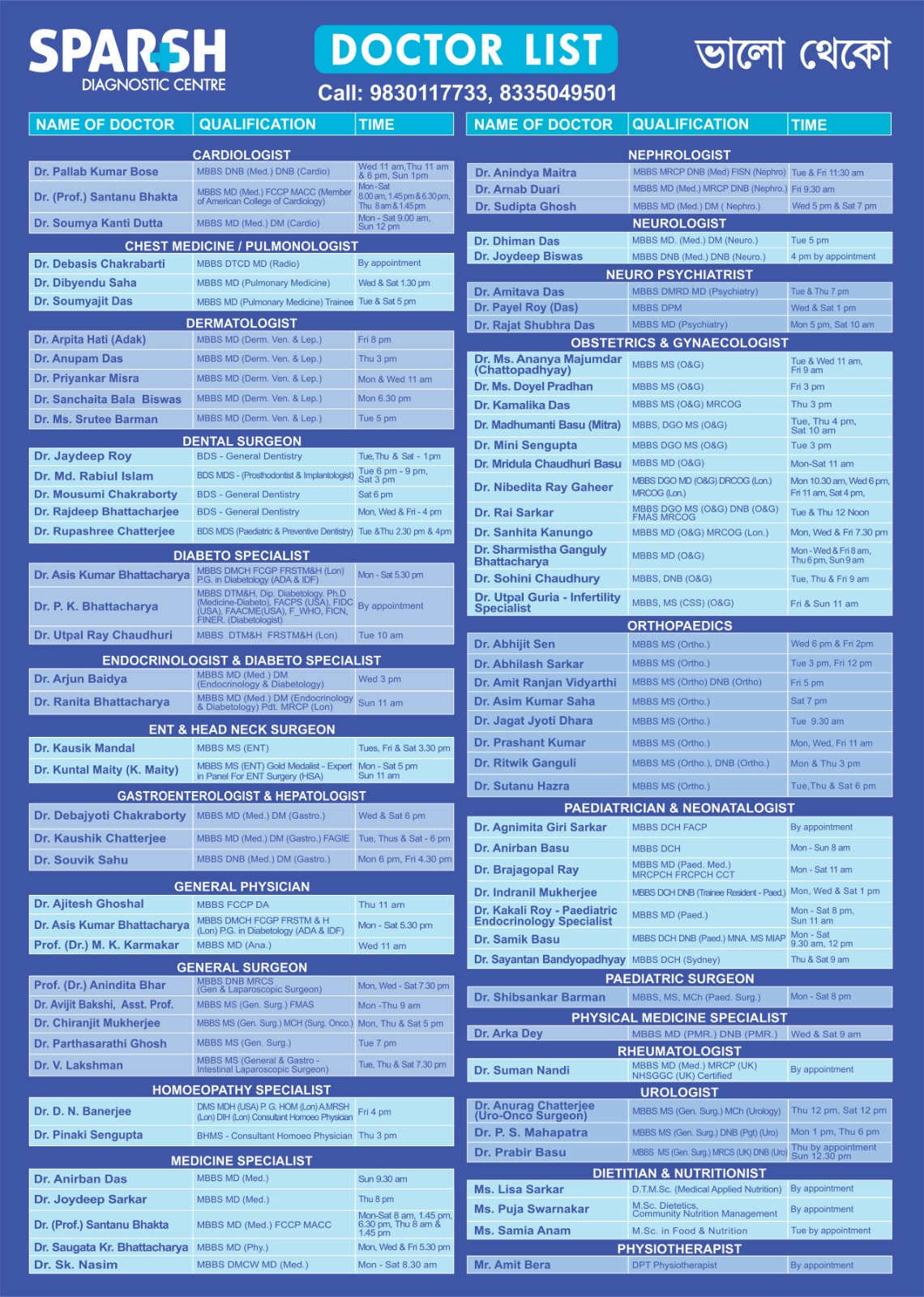
Sparsh Diagnostic Centre Doctor List
![]()