Cancer treatment has evolved dramatically over the last few decades. From chemotherapy and radiation to targeted therapy and immunotherapy, modern medicine is increasingly focused on precision and personalization. One of the most revolutionary advances in this space is CAR T-Cell Therapy, a form of immunotherapy that uses the patient’s own immune system to fight cancer.
CAR T-Cell Therapy has shown remarkable success, especially in certain blood cancers that were previously difficult to treat. In this article, we’ll explore what CAR T-Cell Therapy is, how it works, who it’s for, its benefits, risks, cost considerations, and its future potential—all in simple, easy-to-understand language.
What Is CAR T-Cell Therapy?
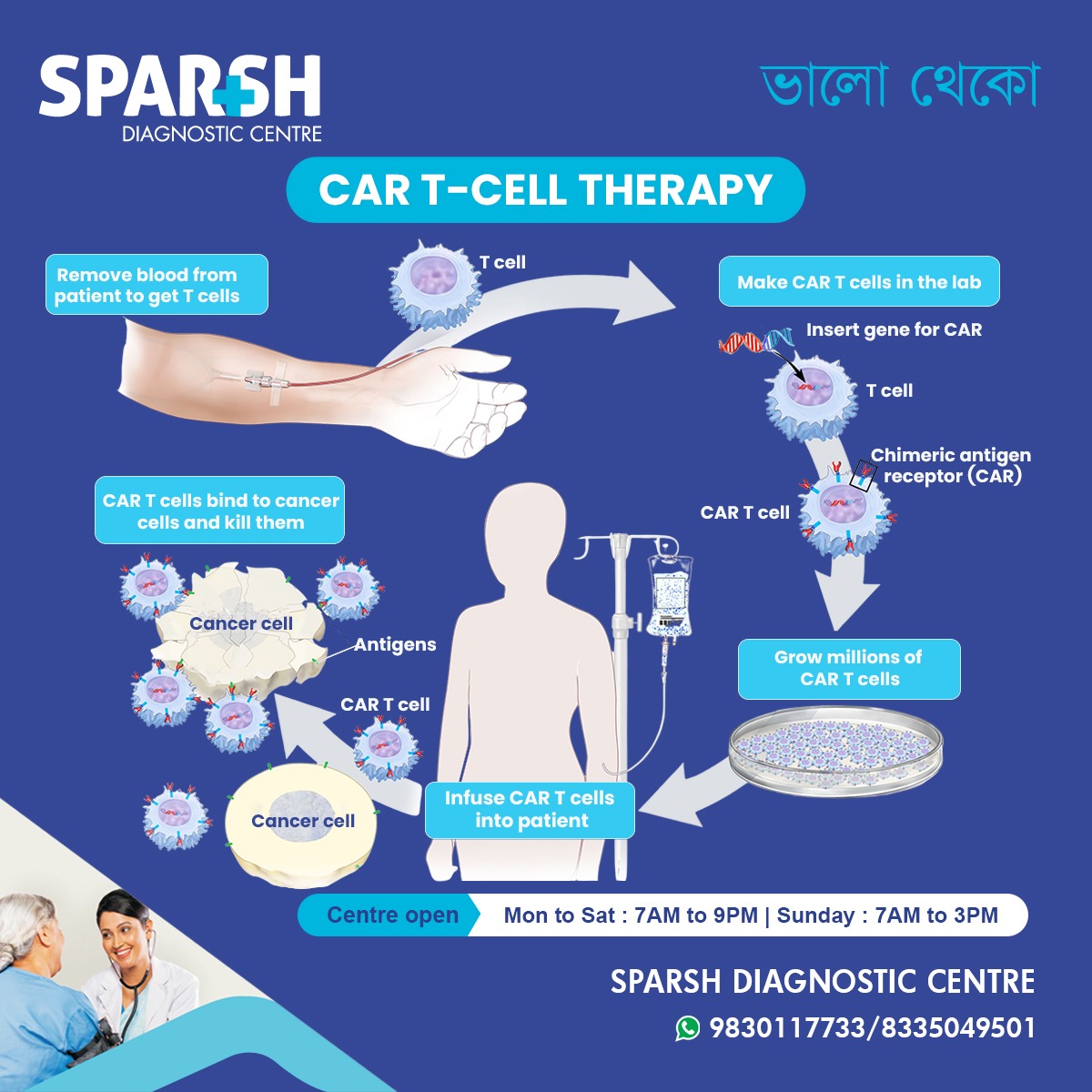
CAR T-Cell Therapy (Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-Cell Therapy) is an advanced cancer treatment that genetically modifies a patient’s T cells—a type of white blood cell—to recognize and destroy cancer cells.
Unlike chemotherapy, which attacks both cancerous and healthy cells, CAR T-Cell Therapy is highly targeted. It trains the immune system to identify cancer cells by specific markers (antigens) found on their surface and then attack them directly.
This personalized approach makes CAR T-Cell Therapy one of the most promising treatments in modern oncology.
Understanding T Cells and the Immune System
To understand CAR T-Cell Therapy, it helps to know a bit about T cells:
T cells are a key part of the immune system
They help identify and destroy infected or abnormal cells
Cancer cells often evade T cells by disguising themselves
CAR T-Cell Therapy overcomes this problem by re-engineering T cells so they can clearly recognize cancer cells and eliminate them.
How Does CAR T-Cell Therapy Work?
CAR T-Cell Therapy is a multi-step process that typically takes several weeks. Here’s how it works step by step:
1. Collection of T Cells
Blood is drawn from the patient using a process called leukapheresis. During this procedure:
Blood is removed from the body
T cells are separated
The remaining blood components are returned to the patient
2. Genetic Modification in the Lab
The collected T cells are sent to a specialized laboratory where:
A new gene is inserted into the T cells
This gene helps create a Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR)
The CAR allows T cells to recognize cancer-specific antigens
3. Multiplication of CAR T Cells
Once modified, the CAR T cells are:
Grown and multiplied in large numbers
Tested for safety and effectiveness
4. Pre-Treatment Chemotherapy
Before infusion, patients usually receive low-dose chemotherapy to:
Reduce existing immune cells
Create space for CAR T cells to expand and function
5. Infusion of CAR T Cells
The CAR T cells are infused back into the patient through an IV, similar to a blood transfusion.
6. Cancer Cell Destruction
Once inside the body:
CAR T cells identify cancer cells
Bind to cancer antigens
Destroy the cancer cells
Continue multiplying to provide ongoing protection
Types of Cancer Treated with CAR T-Cell Therapy
Currently, CAR T-Cell Therapy is primarily used for blood cancers, including:
Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL)
Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma (DLBCL)
Follicular Lymphoma
Mantle Cell Lymphoma
Multiple Myeloma
Research is ongoing to expand its use to solid tumors such as breast cancer, lung cancer, and brain tumors.
Benefits of CAR T-Cell Therapy
CAR T-Cell Therapy offers several unique advantages:
1. Personalized Treatment
Since the therapy uses the patient’s own cells, it is highly individualized.
2. High Response Rates
Many patients with relapsed or treatment-resistant cancers have achieved complete remission.
3. Long-Lasting Effects
CAR T cells can remain active in the body for months or even years, providing ongoing cancer surveillance.
4. Targeted Action
CAR T cells focus specifically on cancer cells, reducing damage to healthy tissues compared to traditional chemotherapy.
Risks and Side Effects of CAR T-Cell Therapy
While CAR T-Cell Therapy can be life-saving, it is not without risks. Side effects can range from mild to severe and require close medical monitoring.
Cytokine Release Syndrome (CRS)
The most common side effect, CRS occurs when CAR T cells release large amounts of immune signaling molecules.
Symptoms include:
Difficulty breathing
Organ dysfunction (in severe cases)
Neurological Side Effects
Some patients may experience:
Increased Infection Risk
Since CAR T-Cell Therapy affects the immune system, patients may be more prone to infections temporarily.
Low Blood Cell Counts
This can increase the risk of bleeding, anemia, and infections.
Who Is Eligible for CAR T-Cell Therapy?
CAR T-Cell Therapy is usually recommended for patients who:
Have certain blood cancers
Have not responded to standard treatments
Have experienced cancer relapse
Are physically fit enough to tolerate the therapy
Eligibility is determined by oncologists based on cancer type, stage, overall health, and prior treatments.
CAR T-Cell Therapy in India
CAR T-Cell Therapy is increasingly becoming available in India, with several hospitals and research institutions offering this advanced treatment.
Key Points:
India has developed indigenous CAR T therapies, making treatment more affordable
Costs in India are significantly lower than in Western countries
Specialized centers with trained oncologists are essential
This development has made CAR T-Cell Therapy more accessible to patients who previously could not afford it.
Cost of CAR T-Cell Therapy
CAR T-Cell Therapy is one of the most expensive cancer treatments due to its complexity.
Approximate Cost:
Internationally: ₹3–4 crore ($ 300,000 – $ 500,000)
In India: ₹30–50 lakh (varies by center and therapy type) ($32,000 – $ 55,000)
Costs may include:
Cell collection and modification
Hospital stay
ICU care if needed
Post-treatment monitoring
Financial counseling is often recommended before starting therapy.
Life After CAR T-Cell Therapy
Recovery and follow-up care are crucial after CAR T-Cell Therapy.
Post-Treatment Monitoring Includes:
Regular blood tests
Monitoring for late side effects
Infection prevention
Long-term cancer surveillance
Many patients experience significant improvement in quality of life once they recover from initial side effects.
Future of CAR T-Cell Therapy
The future of CAR T-Cell Therapy looks extremely promising.
Ongoing Research Focuses On:
Treating solid tumors
Reducing side effects
Making therapy faster and more affordable
Developing “off-the-shelf” CAR T cells
Combining CAR T therapy with other immunotherapies
As research advances, CAR T-Cell Therapy is expected to become more widely available and effective.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. Is it a cure for cancer?
CAR T-Cell Therapy can lead to long-term remission and, in some cases, a functional cure, but results vary depending on cancer type and patient factors.
2. How long does it take?
The entire process—from cell collection to infusion—usually takes 3 to 6 weeks, followed by close monitoring.
3. Is it painful?
The infusion itself is not painful, but side effects such as fever or fatigue may occur during recovery.
4. Can it be repeated?
In some cases, retreatment may be possible, but this depends on individual response and medical evaluation.
5. Is it safe for elderly patients?
Age alone is not a barrier. Overall health and fitness are more important factors.
6. Does it cause hair loss?
Hair loss is uncommon unless chemotherapy is used as part of pre-treatment conditioning.
7. How successful is it?
Success rates are high in certain blood cancers, with remission rates ranging from 60–90% in eligible patients.
CAR T-Cell Therapy represents a major milestone in cancer treatment, offering hope to patients with aggressive or treatment-resistant cancers. By harnessing the power of the immune system, this innovative therapy has transformed outcomes for many individuals who previously had limited options.
As research continues and accessibility improves—especially in countries like India—CAR T-Cell Therapy is poised to play an even greater role in the future of oncology.
If you or a loved one is exploring advanced cancer treatment options, consulting a specialized oncology or diagnostic center can help determine whether CAR T-Cell Therapy is the right choice.
#BhaloTheko
Disclaimer:
No content on this site, regardless of date, should ever be used as a substitute for direct medical advice from your doctor or other qualified clinician.
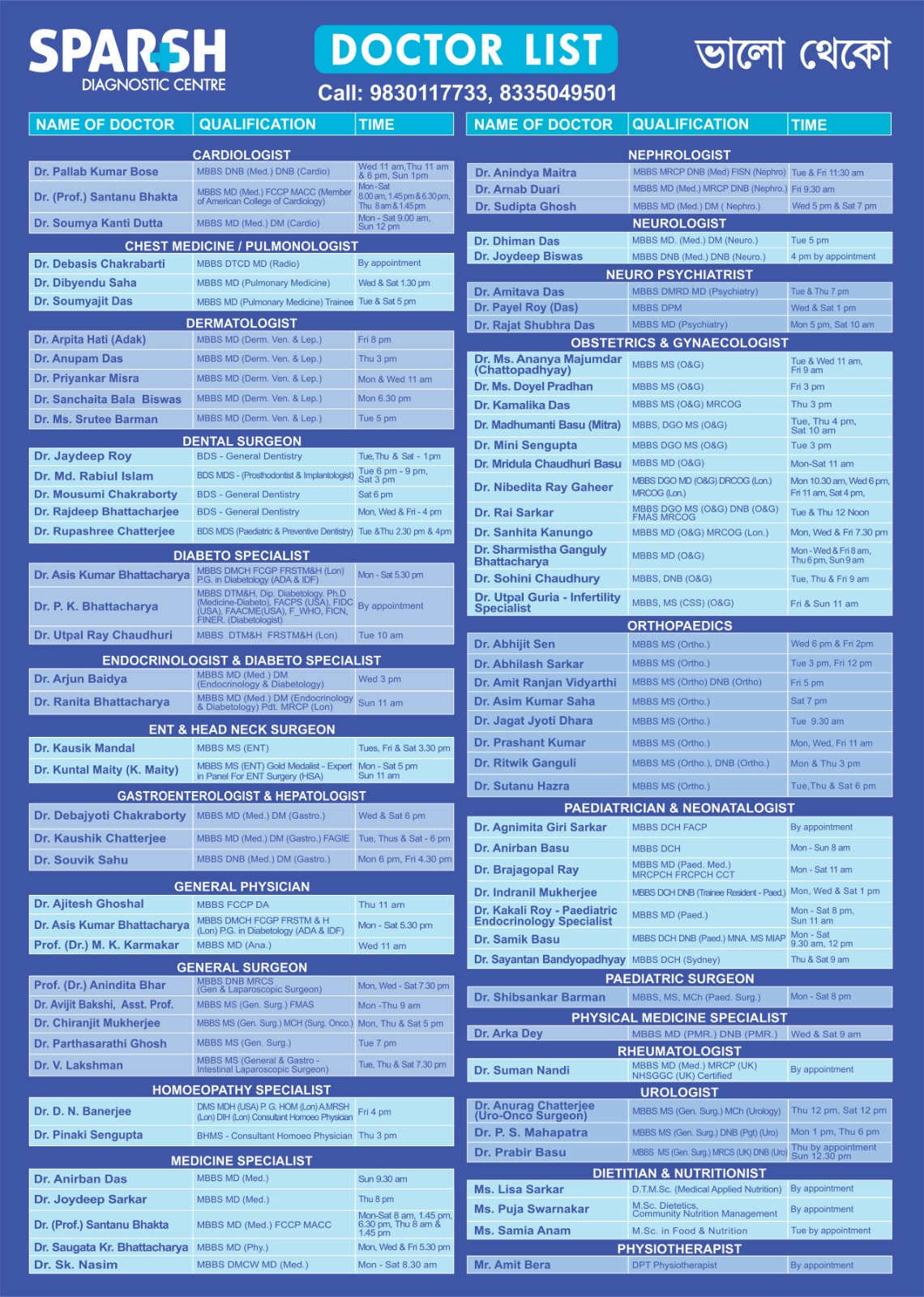
Sparsh Diagnostic Centre Doctor List
![]()




[…] boosts the body’s immune system to help it fight cancer. Checkpoint inhibitors, CAR T-cell therapy, and other forms of immunotherapy are being increasingly used to treat lymphoma, particularly in […]